This story appears on the Argus Media website from October 8, 2021.
By Stephen Cunningham
US oil producers are turning to an unexpected source to help solve the environmental problem of excess natural gas — cryptocurrency miners.
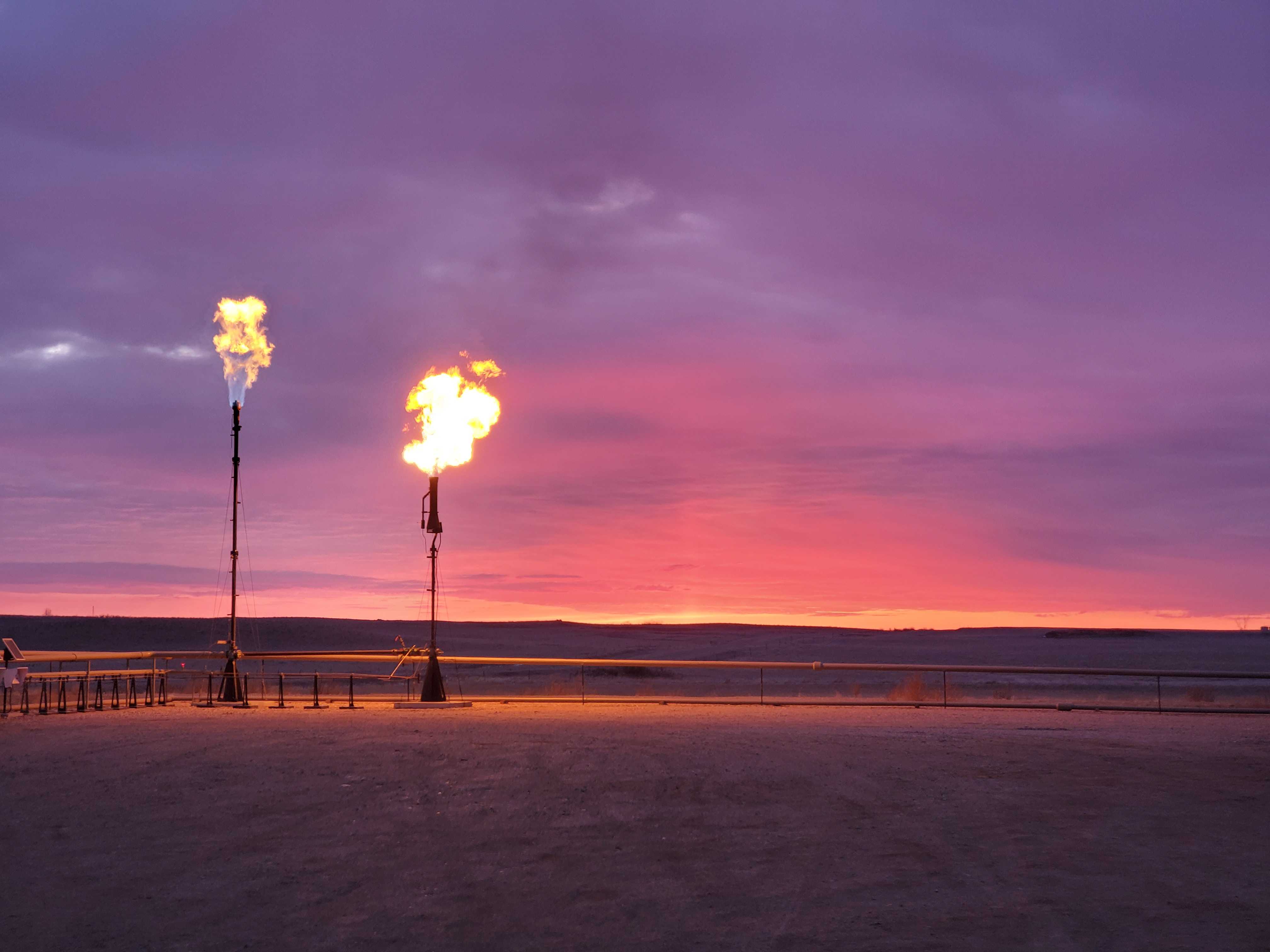
On remote well pads dotted across the Bakken shale play of North Dakota and Montana, shipping container-sized data centers packed with computers power energy-intensive operations of Bitcoin miners. Their computers, running around the clock to earn crypto tokens by authenticating digital transactions, are powered by natural gas-fired generators, running on gas from the oil wells that would otherwise be flared on site.
Mining for virtual currencies has attracted widespread criticism — from environmental groups to tech entrepreneur Elon Musk — because it uses vast quantities of energy, more than some nations use in a year. That has led crypto miners to try and cut down on their energy use, or at least find ways to shrink their carbon footprint.
In the Bakken, they are able to capitalize on an abundance of surplus natural gas — a common byproduct of oil production — that would otherwise be burned off given a lack of pipeline infrastructure to take it to market. The environmentally harmful practice of flaring has come under intense scrutiny from regulators, climate campaigners and investors, including fund manager Blackrock.
Companies tapping surplus gas to run their cypto-mining computer banks see a double benefit — reducing the negative impacts of gas flaring and cutting their carbon footprint.
Denver-based Crusoe Energy operates 44 data centers in Montana, North Dakota, Wyoming and Colorado, and was due to deploy another 16 units by the end of September. Plans are afoot to start an initial project in the top oil producing Permian basin of Texas and New Mexico later this year before ramping up there in 2022.
"Our systems reduce greenhouse gas emissions by the equivalent of hundreds of thousands of cars in the process, primarily by reducing the amount of methane escaping into the atmosphere from incomplete combustion in flares," company president and co-founder Cully Cavness said.
Crusoe expected to reduce flaring in areas where it is operating by almost 10mn cf/d by the end of September. Its technology lowers CO2-equivalent emissions by as much as 63pc compared with continued flaring.
The company's digital flare mitigation system is also used to support other computing intensive processes, such as artificial intelligence.
The prices of crypto currencies including Bitcoin have fluctuated wildly this year with China banning all related transactions and mining. The Chinese crackdown "plays greatly into the advantage of US-based operators as it makes available hardware for domestic projects and increases the competitiveness of American operations," Cavness said.
Equinor, Devon among crypto-miner customers
Before divesting its Bakken acreage earlier this year, Norway's state-controlled Equinor was one of the producers that sold excess gas to Crusoe and provided the company with space on a well pad for its equipment. Other clients have included Devon Energy, private-equity backed Kraken Oil & Gas, and Canadian oil firm Enerplus.
North Dakota has had targets to curb flaring since 2014, with the industry spending billions trying to solve the problem. While flaring eliminates most methane — a potent greenhouse gas — the process still emits CO2. Flaring rose to 10pc of all gas produced in July, above the current 9pc limit allowed in North Dakota, due to several natural gas processing plants being offline.
As an incentive to curb the practice, North Dakota lawmakers passed legislation earlier this year that offered operators a tax credit for installing gas flaring mitigation systems — like those Crusoe operates. Crusoe qualifies for emissions reduction credits because it uses waste gas to generate electricity that would otherwise have come from the grid.
Texas regulators also have adopted a tougher stance against flaring in recent months, after previously taking a largely hands-off approach.
Jim Wright, one of three Republican commissioners on the Texas Railroad Commission, said recently that companies stuck with unwanted gas should reach out to third parties — including crypto currency miners — who can "eliminate the vast majority of emissions that flaring produces and even pay the operator for the gas."